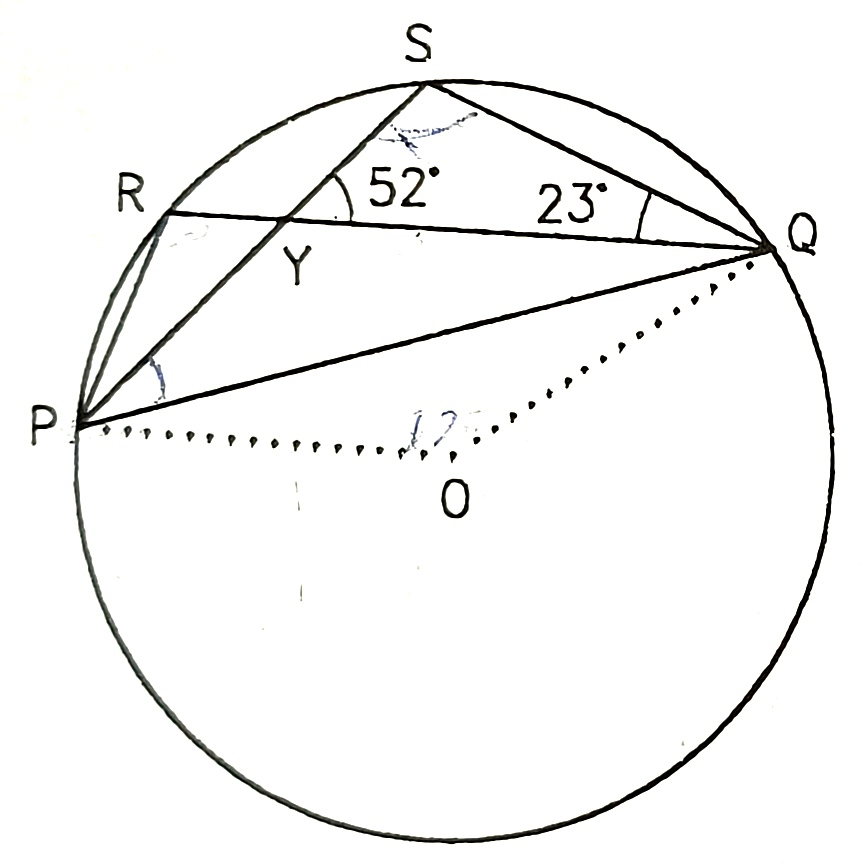
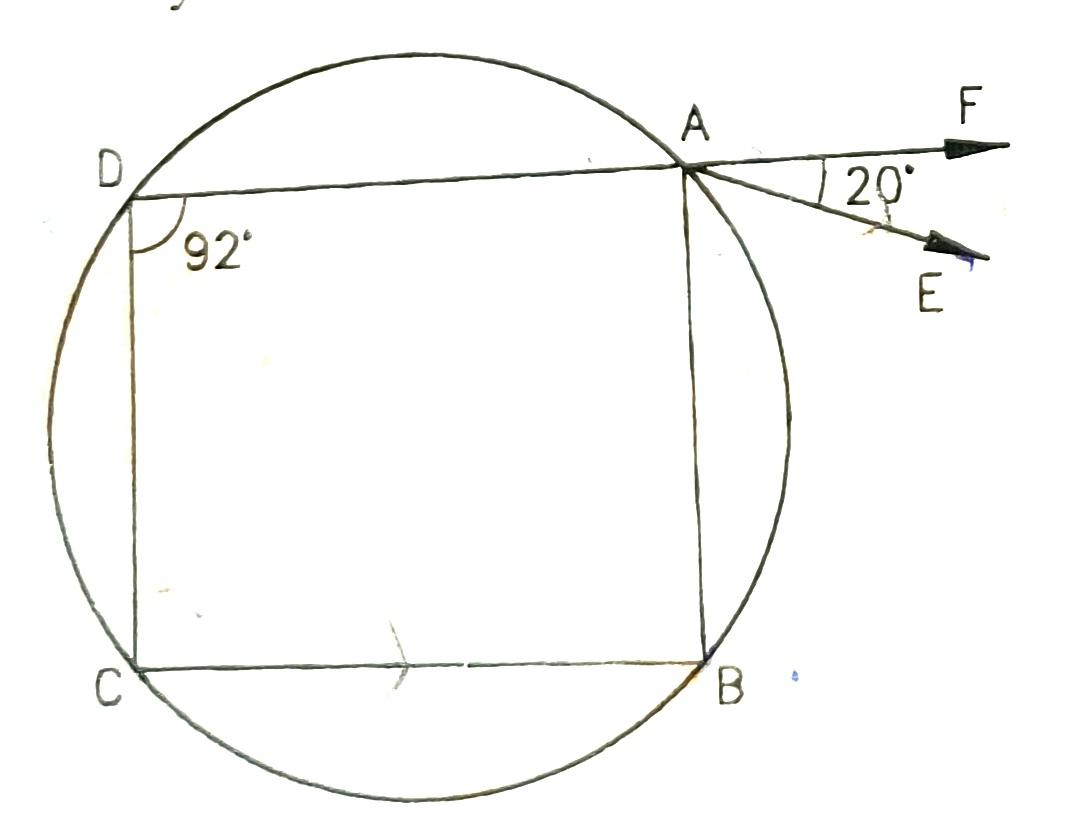
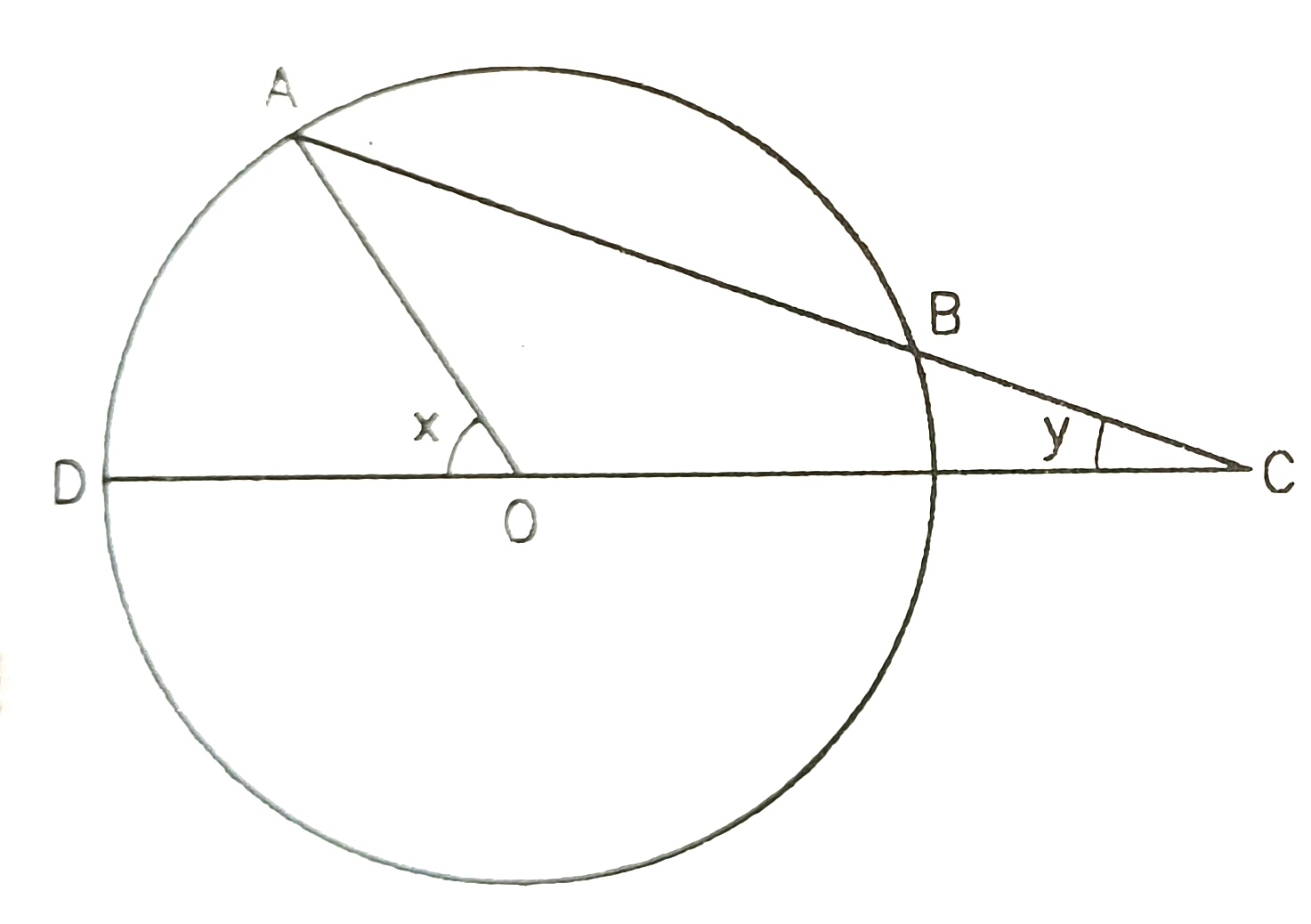
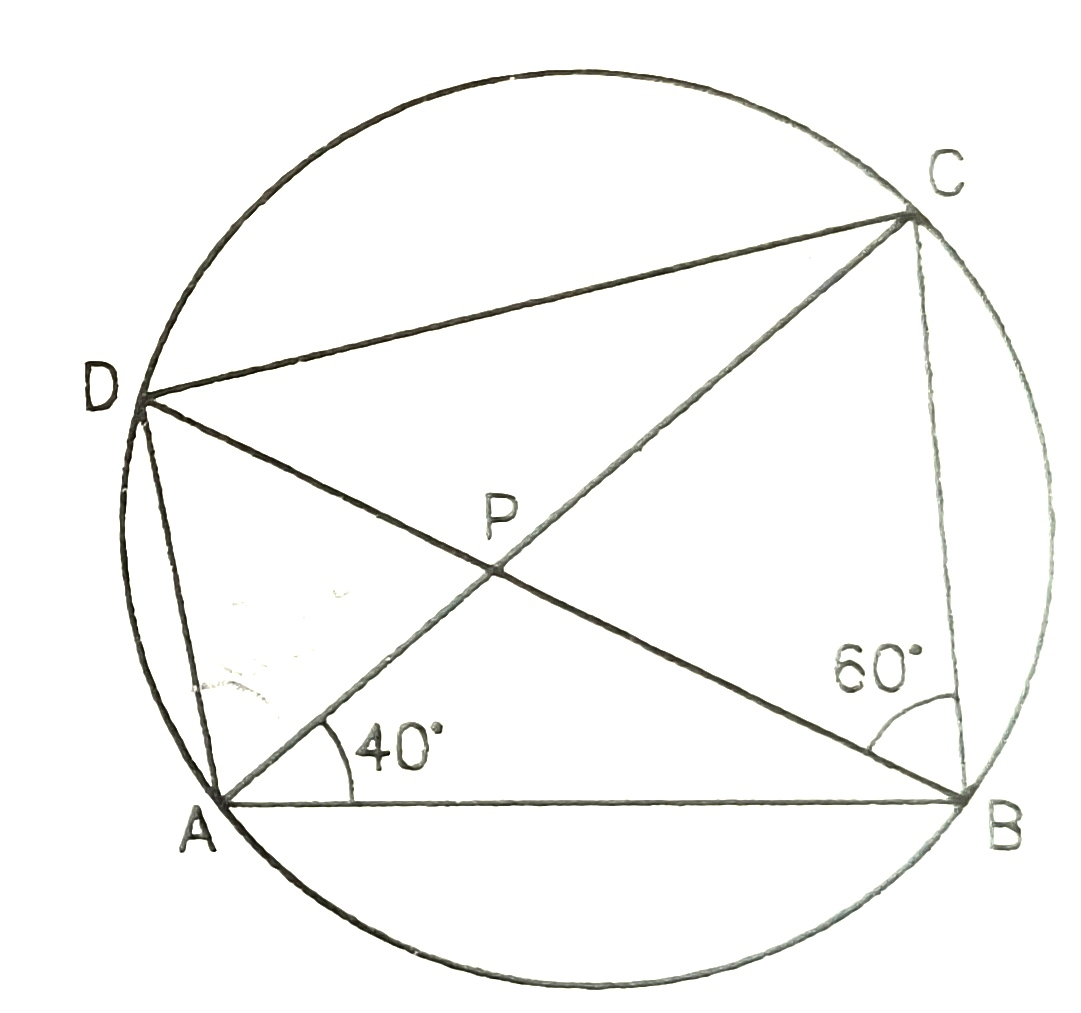
1) Find the value of x of following
110
100
60
60
30
120
100
100
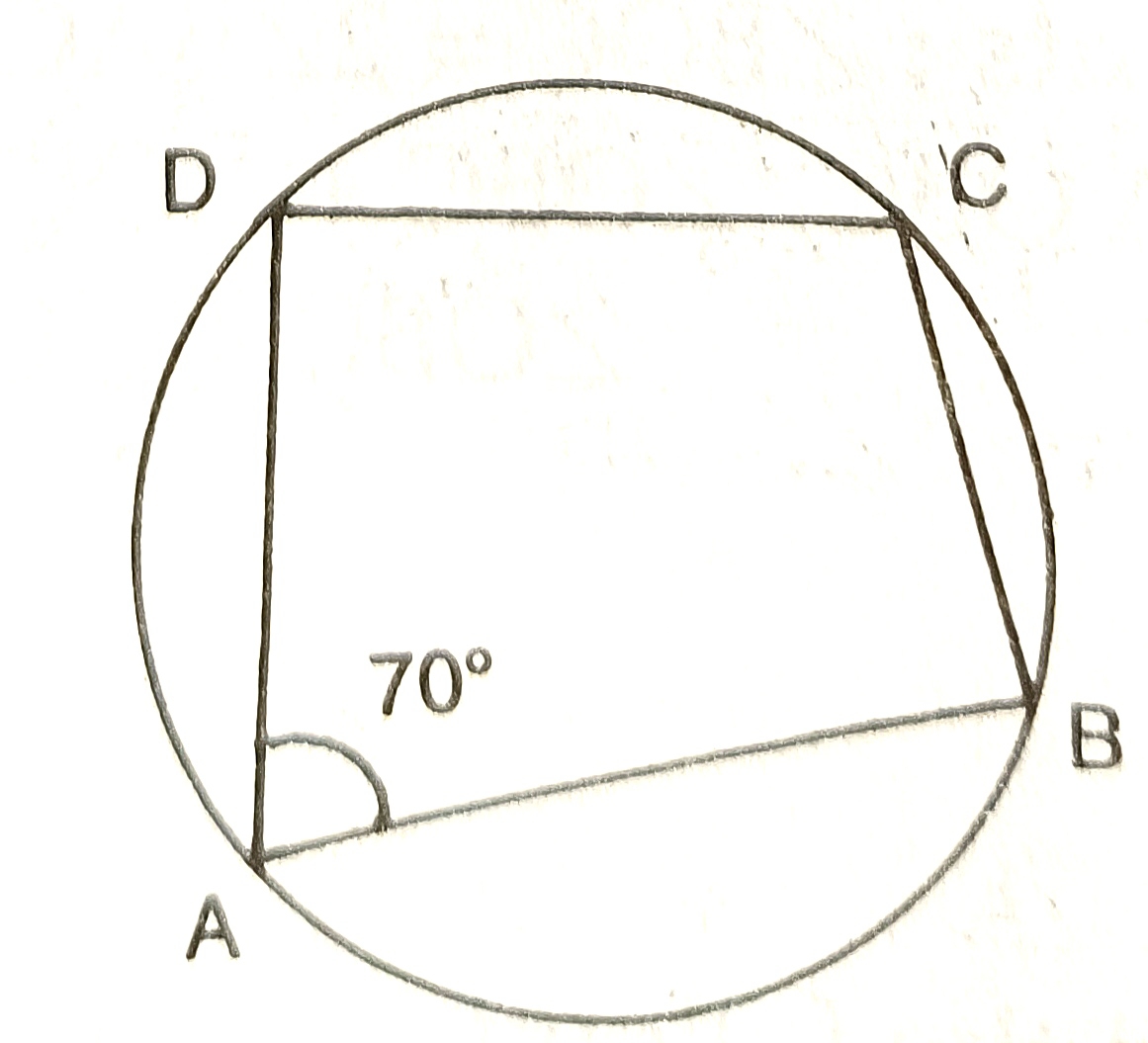
70
100
50
48
40
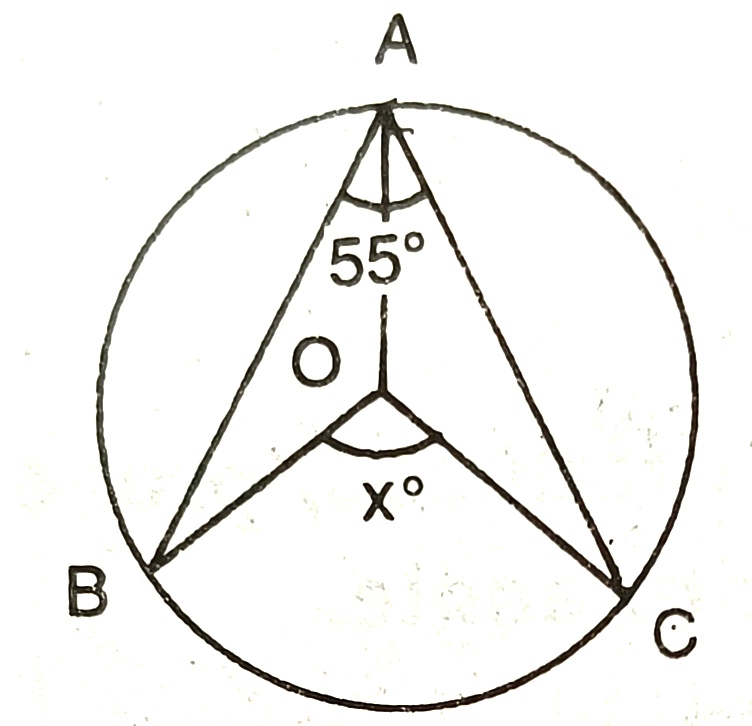
2) If O is the centre of the circle,
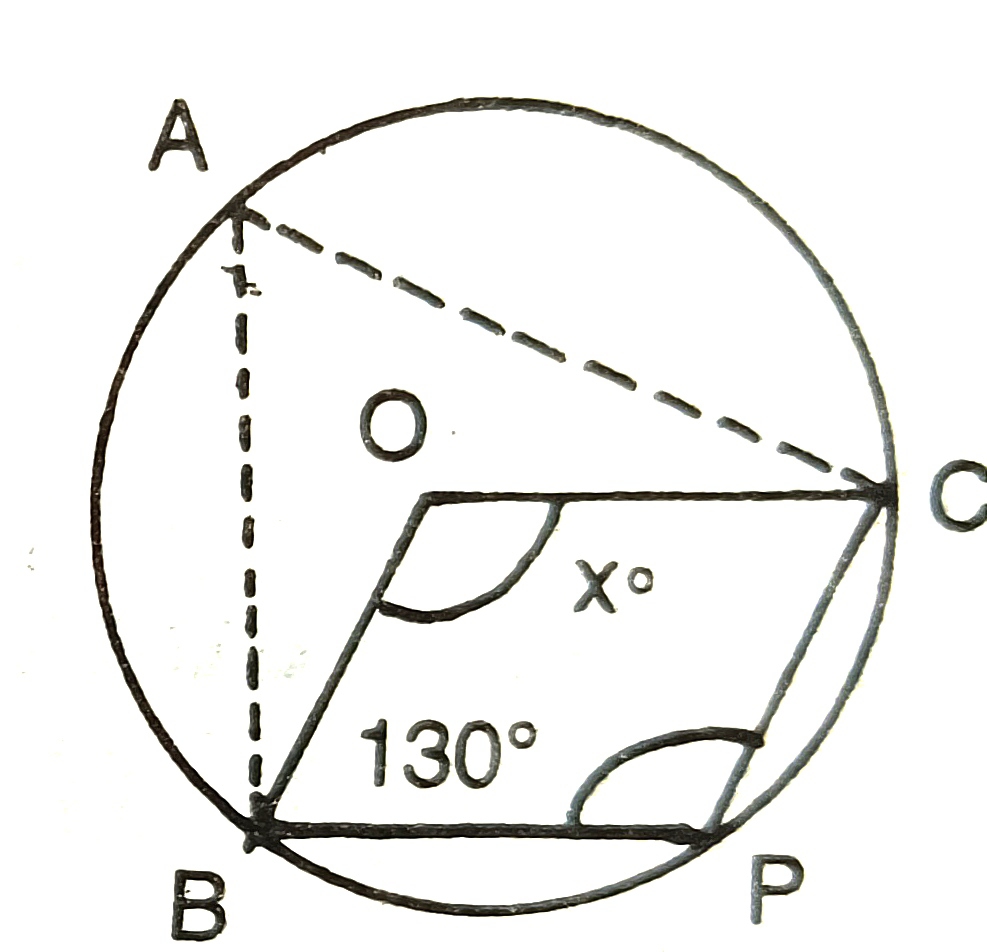
3) If O is the centre of the circle,
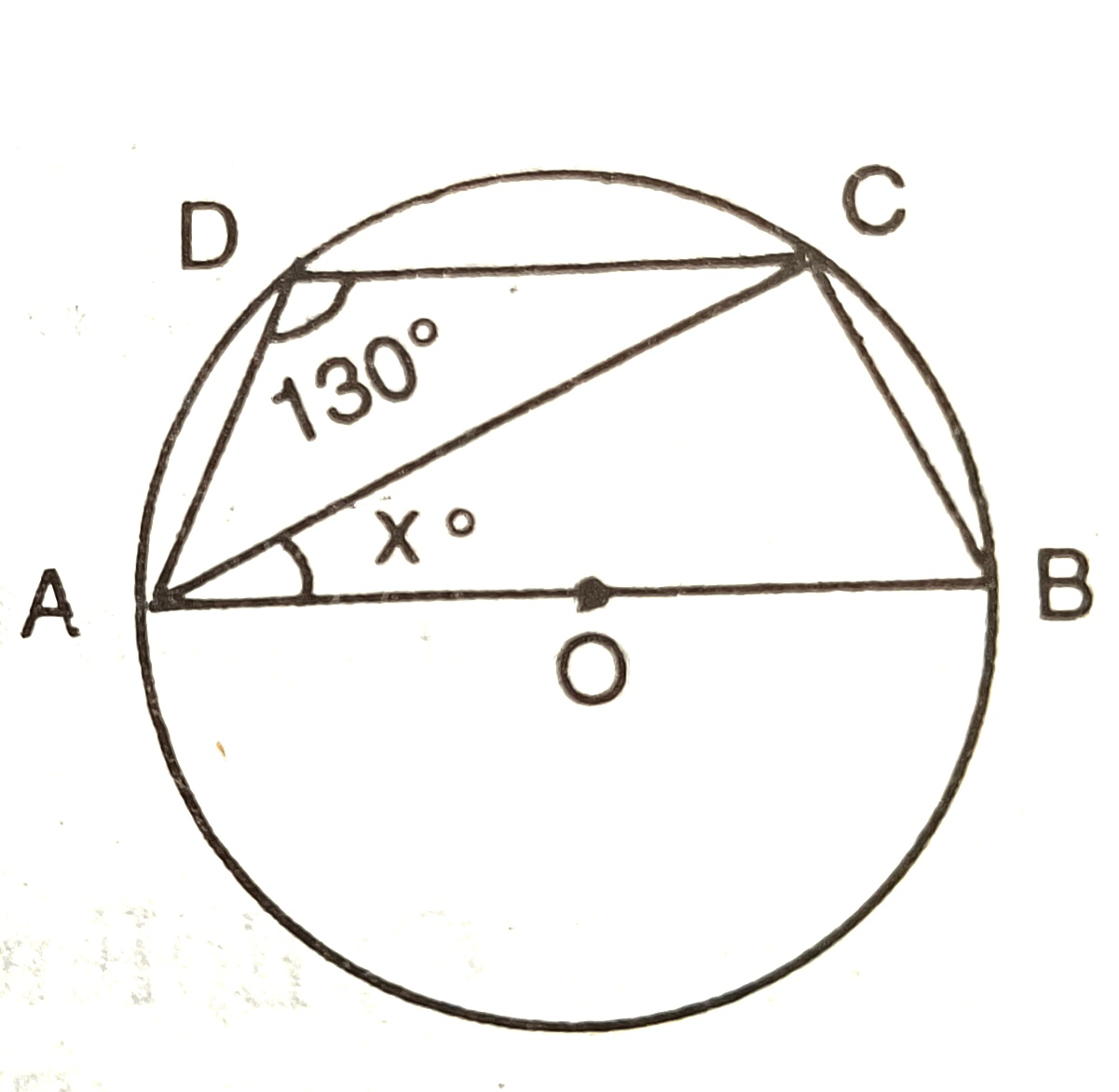
4) If O is the centre of the circle,
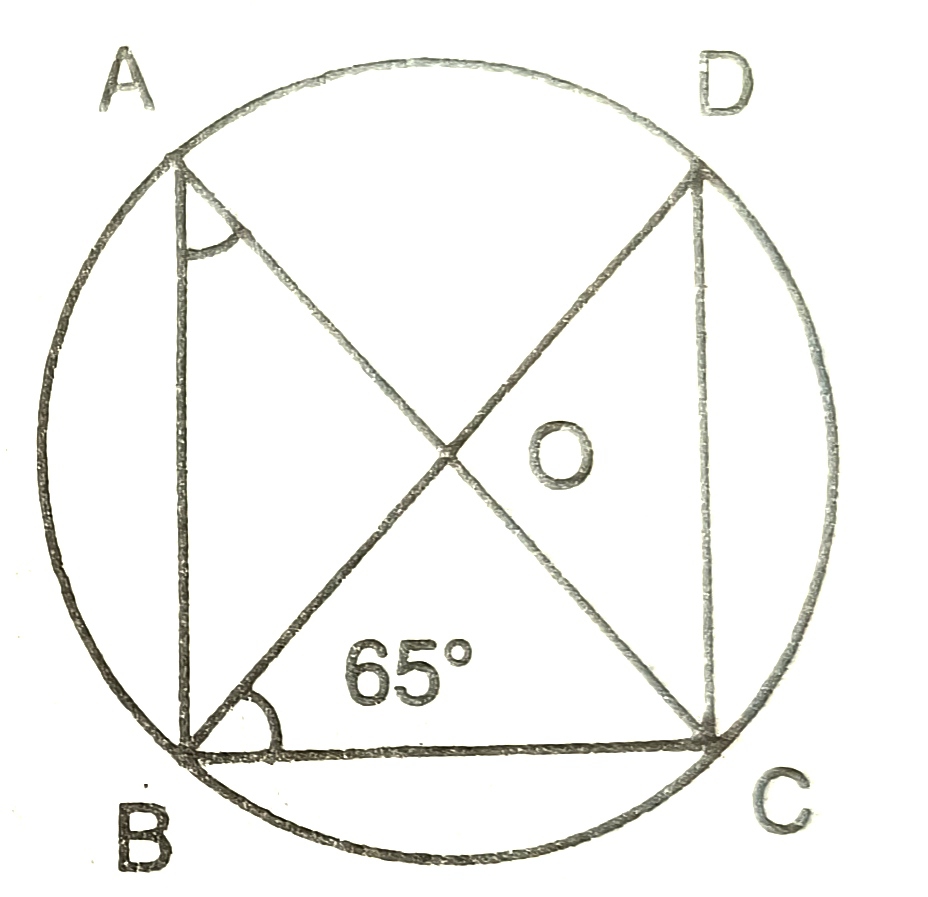
5) If O is the centre of the circle,
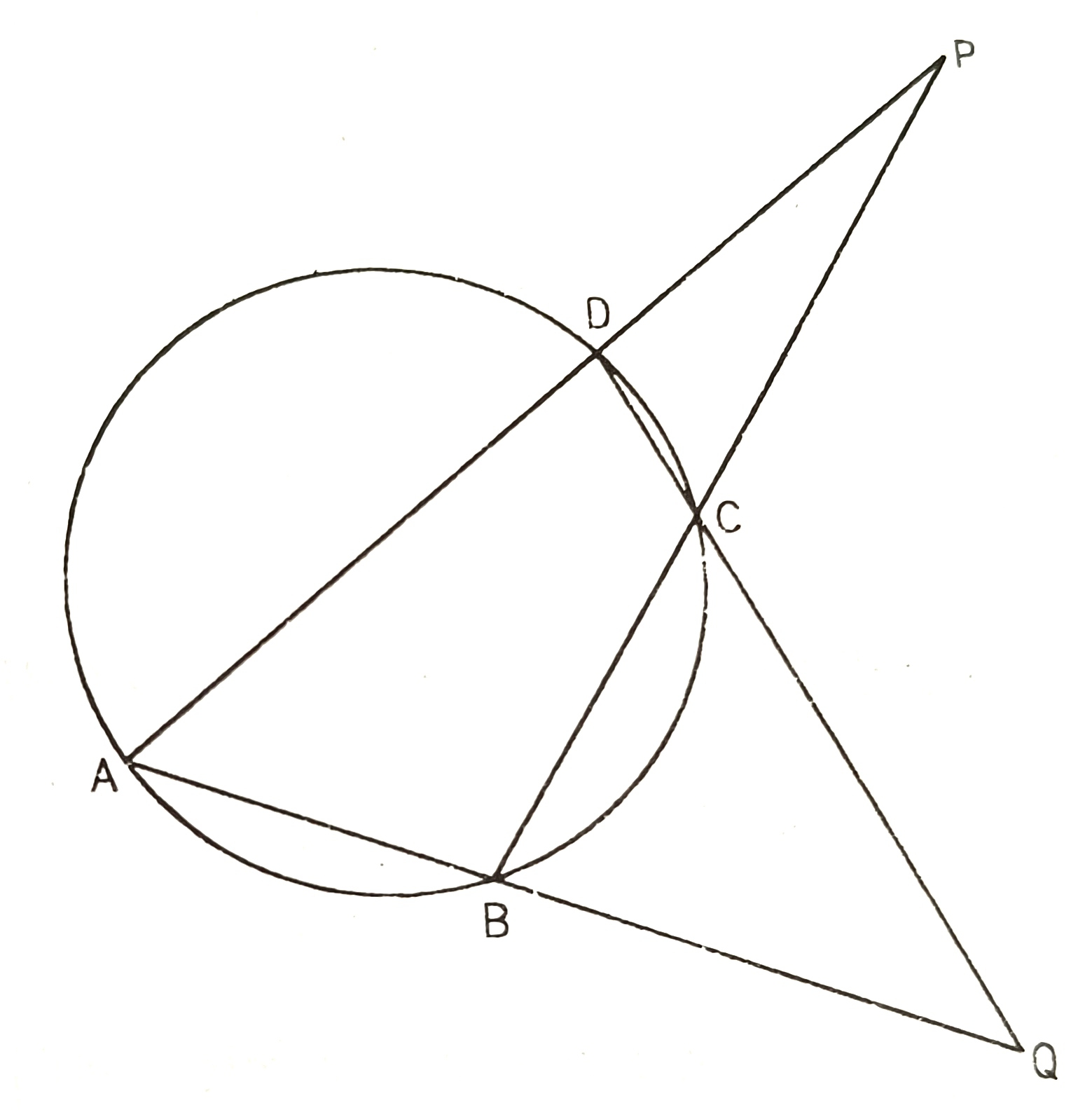
6) In the following figure below,
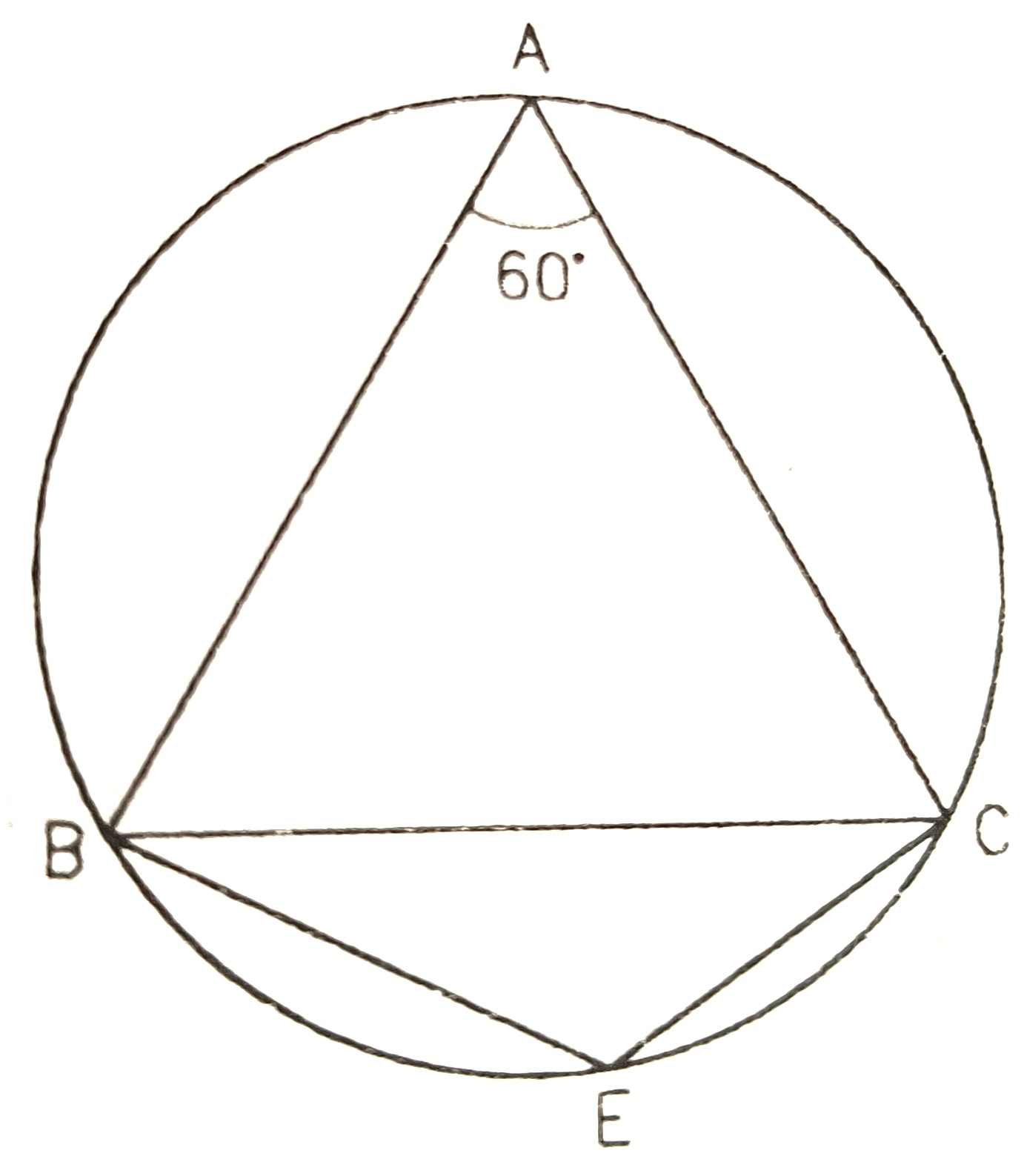
7) In the figure ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle,
8) In the figure measure of arc ABC is 100°
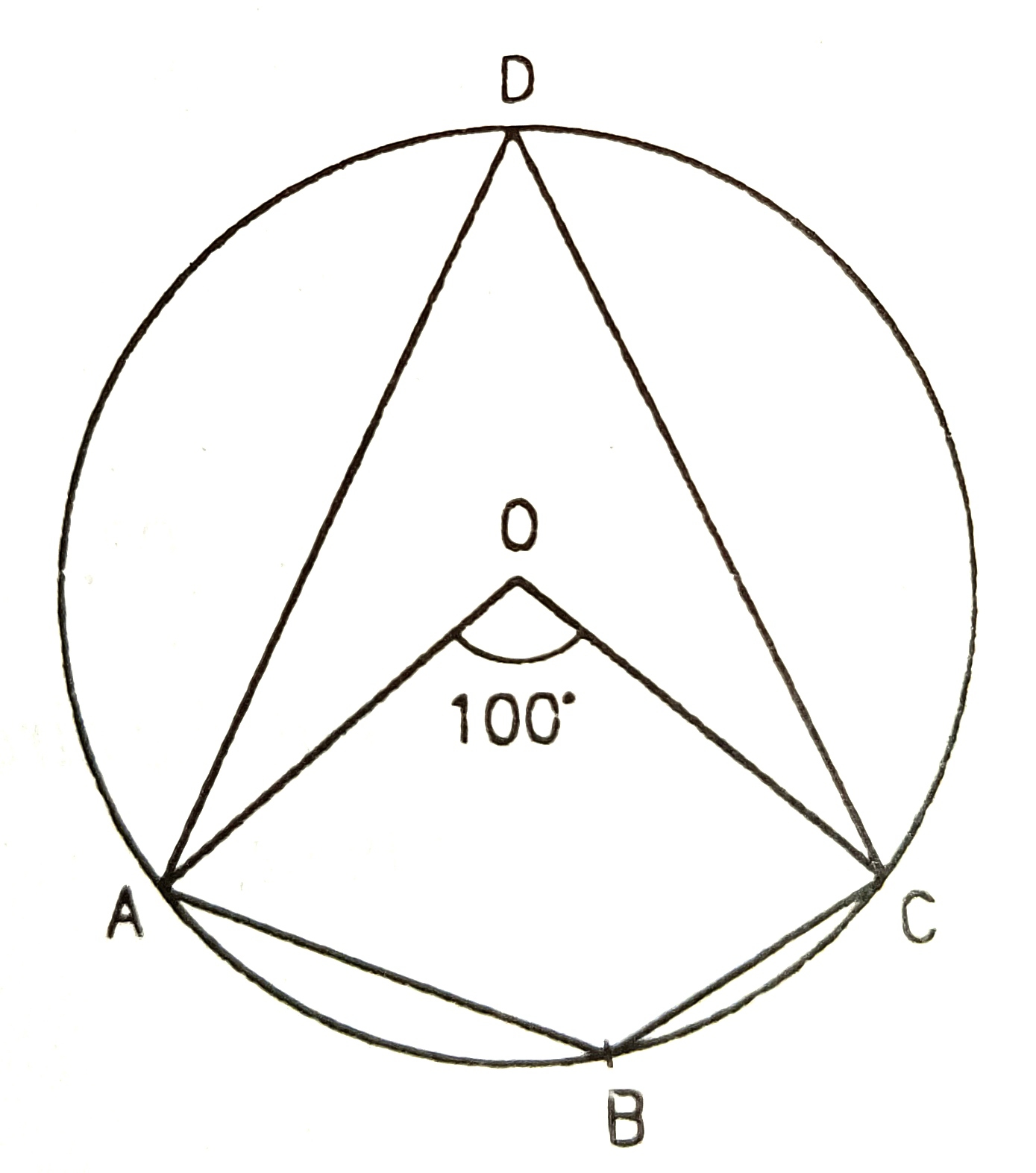
9) figure A,B, C are 3 points on a circle such that the angles subtended by the chord AB and AC at the centre O are 80°, and 120° respectively.
10) In the figure angle BDC=30, ABC=110°,
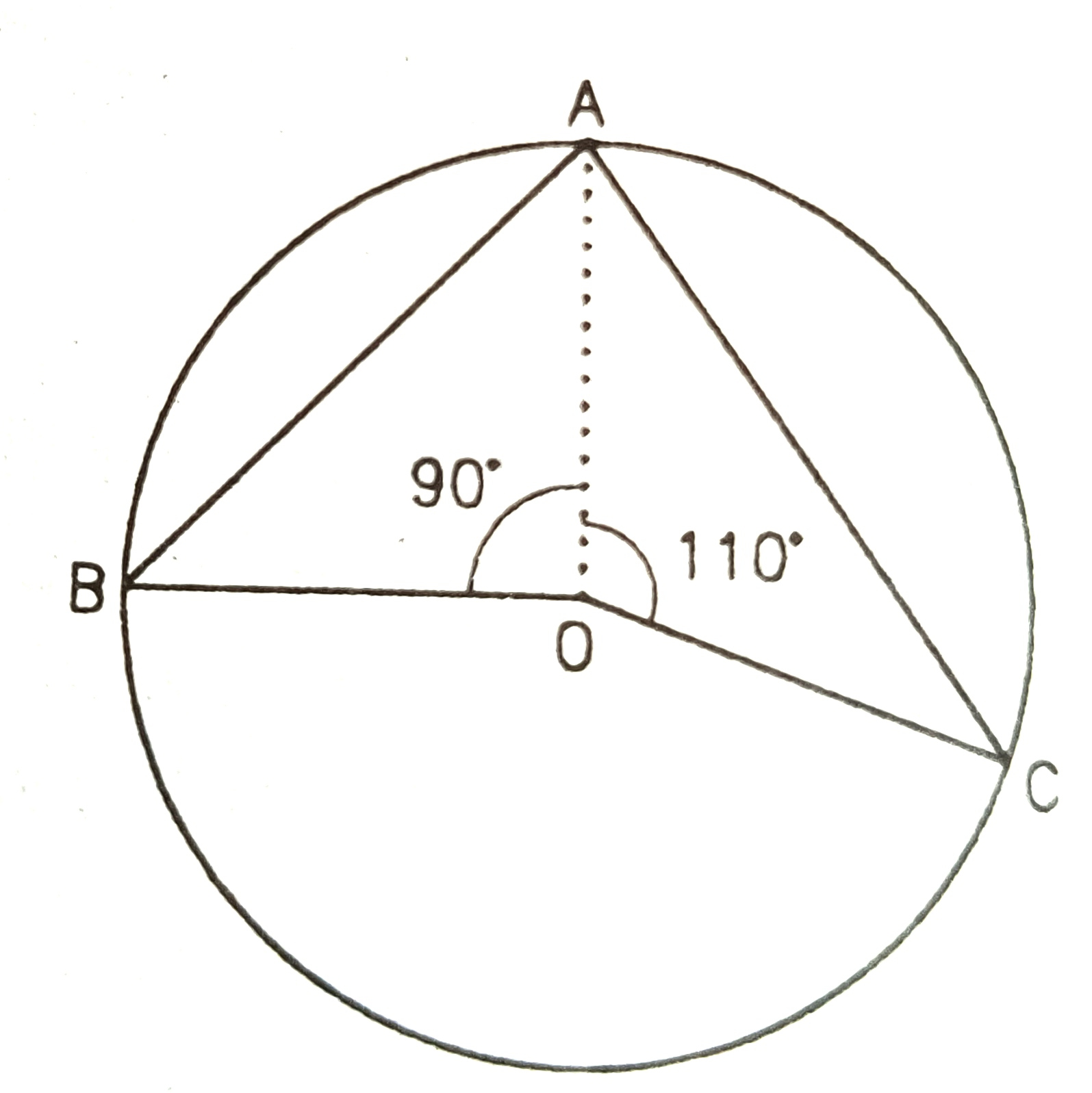
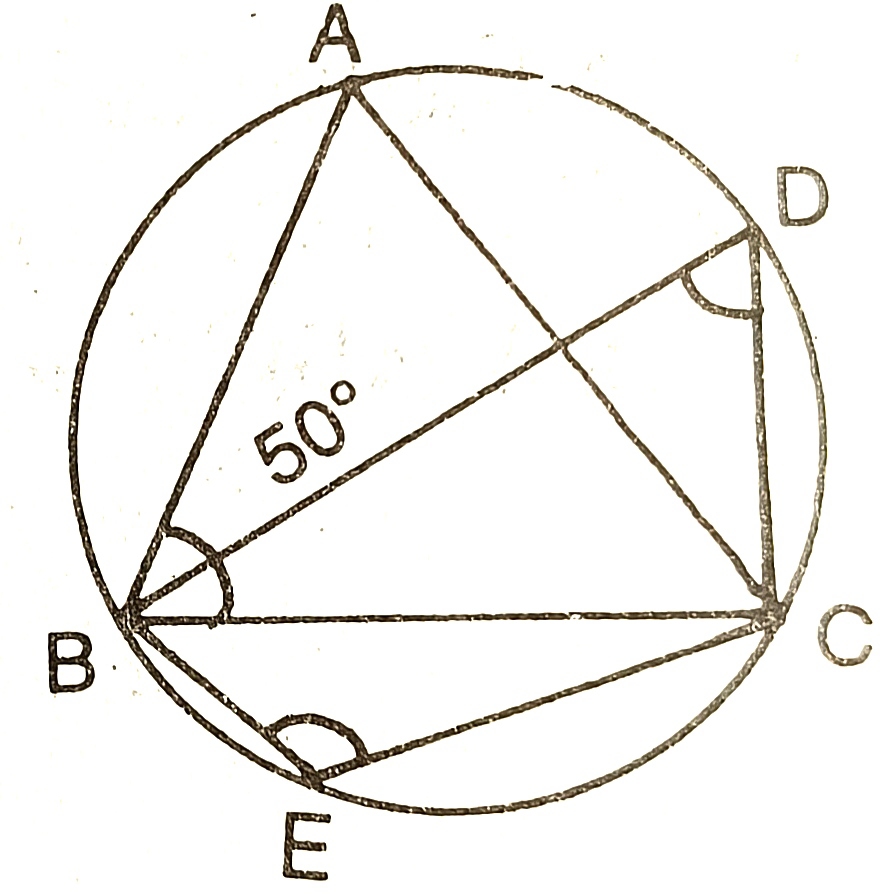
11) In the given figure O is the centre of the circle. If angle BAC =50°,
12) In the figure below, angle BAP and CPD are 40° and 110,
13) In the figure below, angle ABC and BDC are 110 and 30
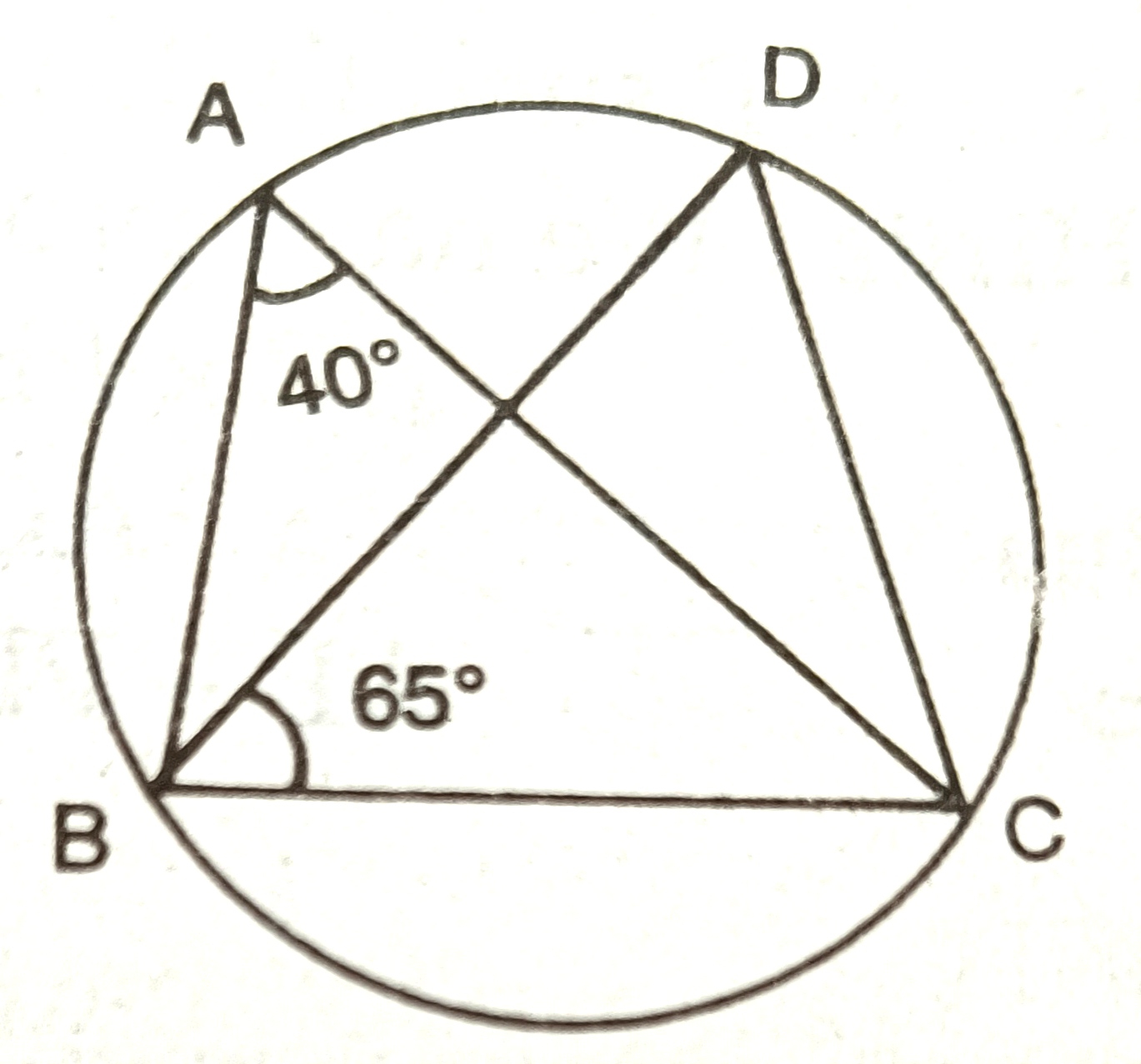
14) In the figure below, angle BAC and DBC are 40° and 65°
15)
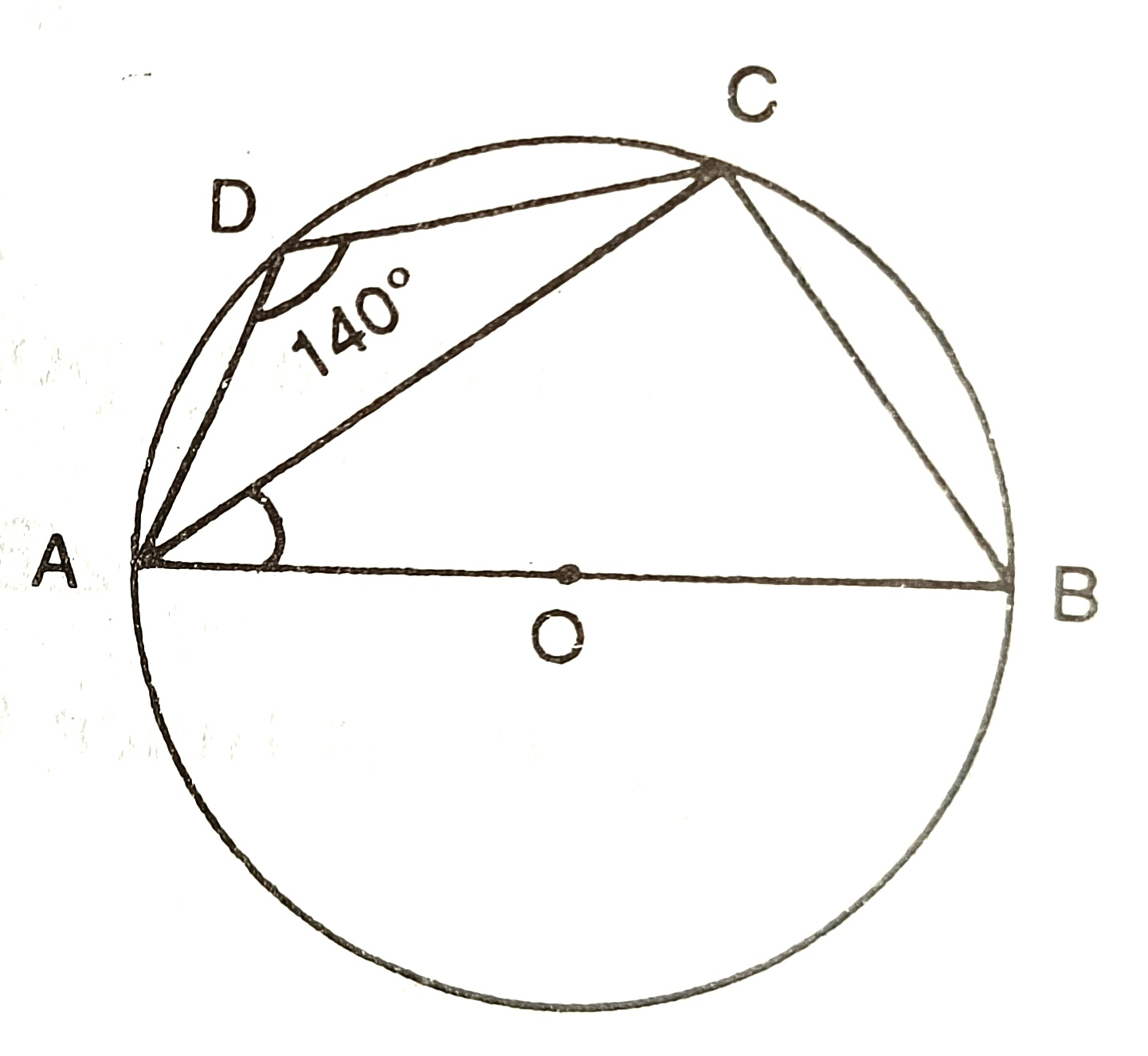
Calculate the measure of angle AOC. 140
16) In figure, A, B and C are three points on a circle such that angles subtended by the chords AB and AC at center O are 90° and 110°. respectively.
17) In figure, A, B, C are 3 points on a circle such that the angles subtended by chords AB and AC at the centre O are 80° and 120° respectively.
18) figure O is the centre of the circle and the measure of arc ABC is 100°.
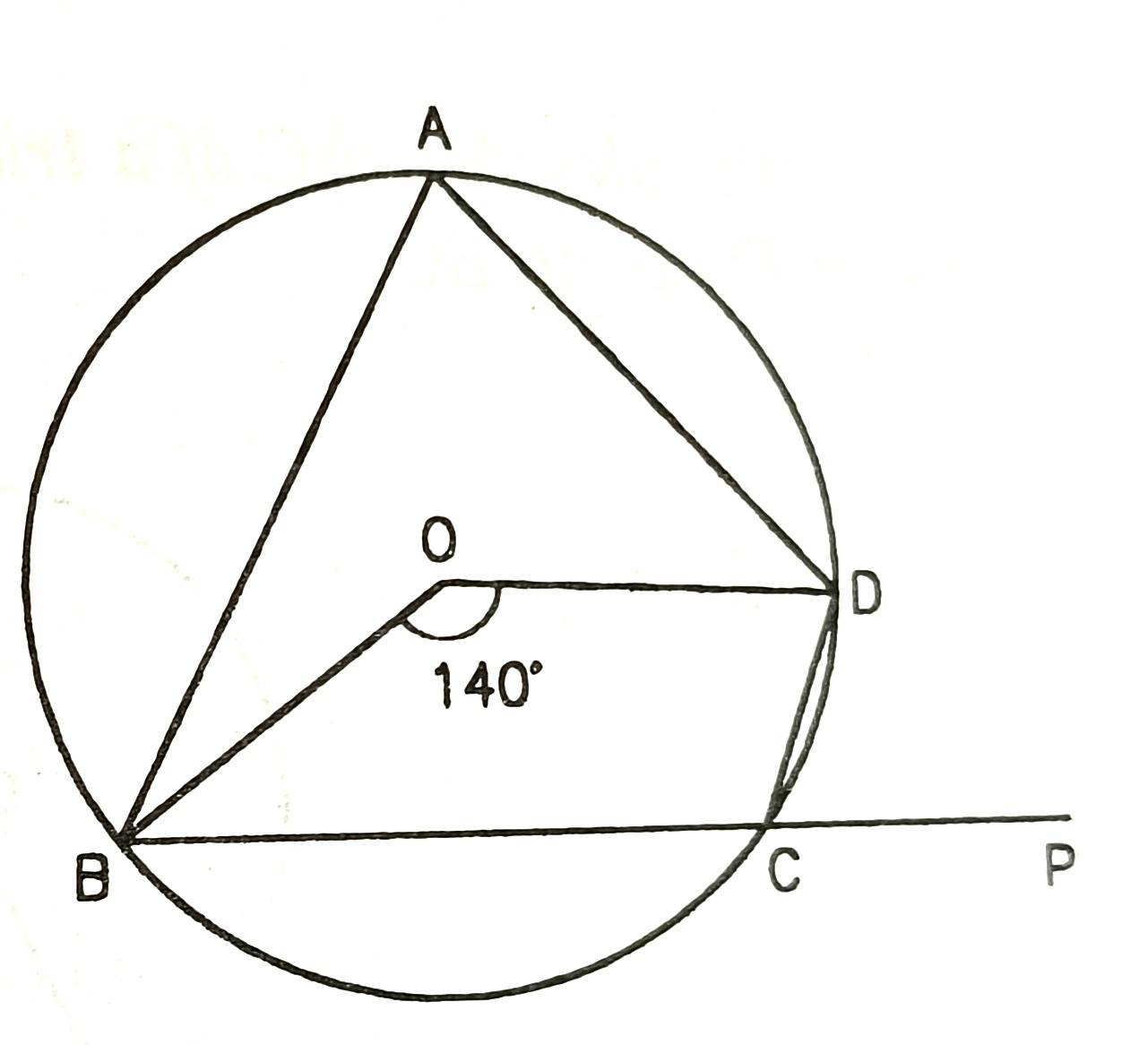
19) itn the figure O is the centre of the circle. The angle subtended by the arc BCD at centre 140°. BC is produced to P.
Find angle PQB were O is the centre of the circle. 48
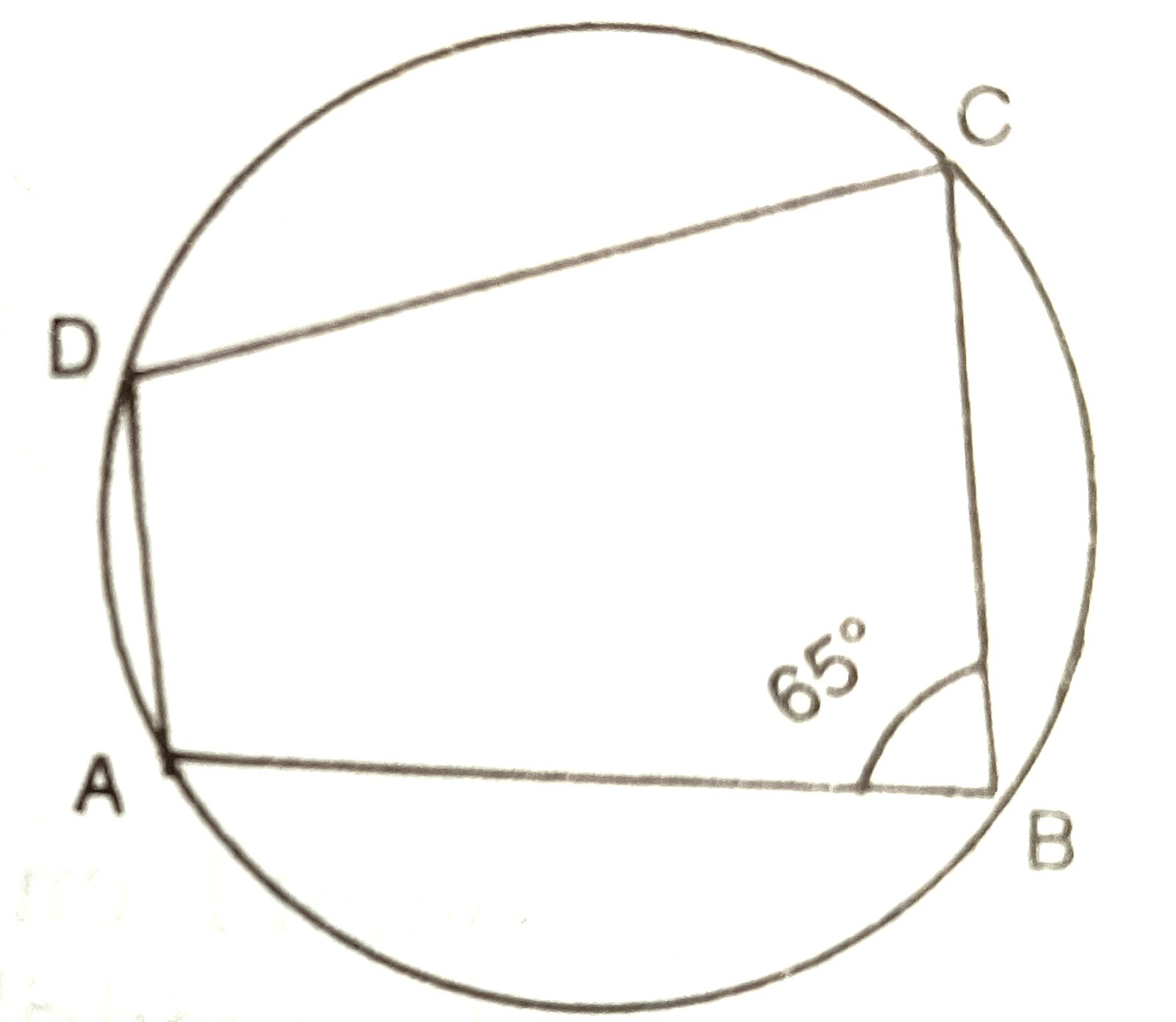
Chord ED is parallel to the diameter AC of the circle. Given angle CBE =65°, find the angle DEC. 25°
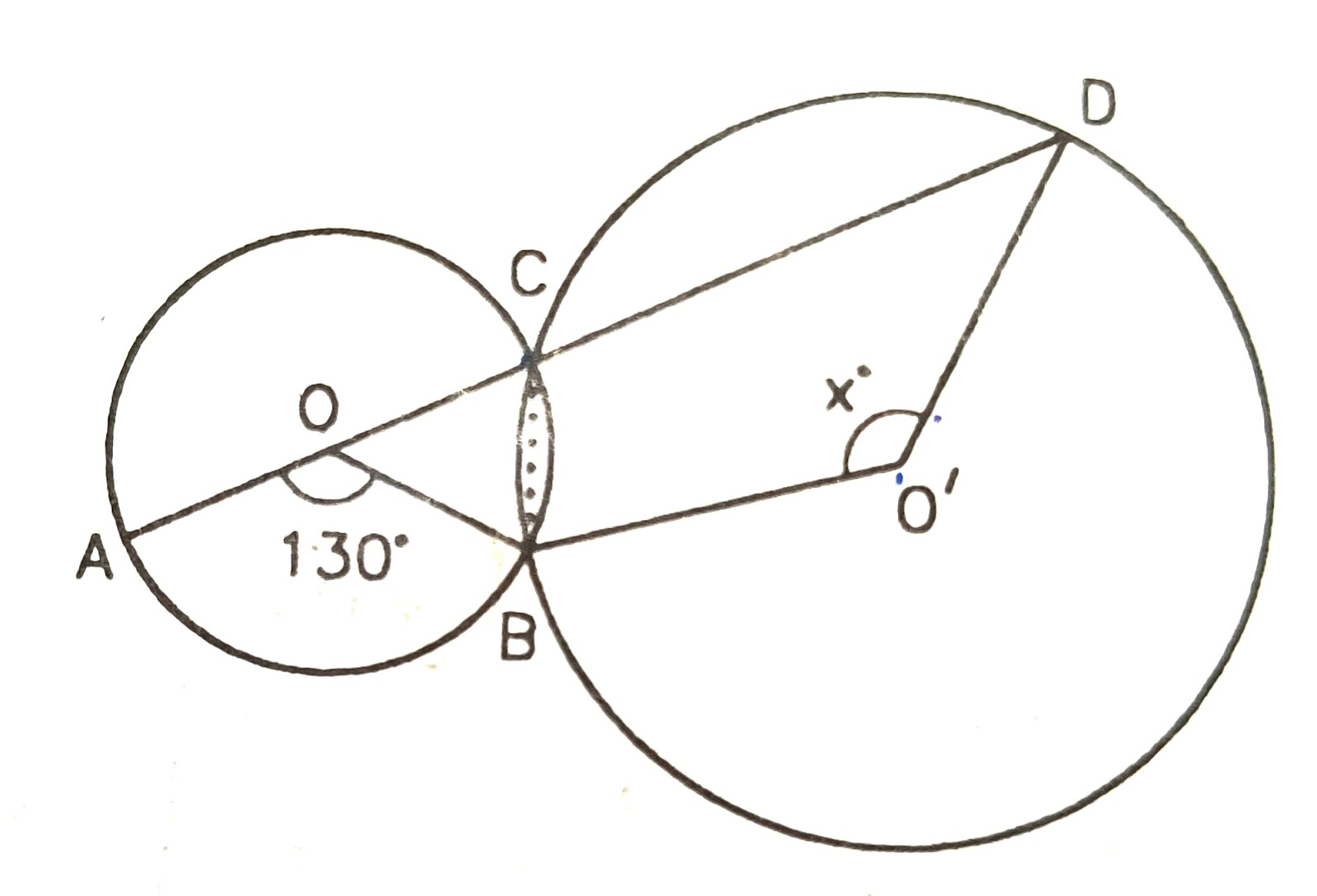
22) in the figure O and O' are centres of two circles intersecting at B and C. ACD is a straight line.
23) In the figure O is the centre and PQ is a diameter. If angle ROS=40°
24) In the figure angle ACB=40, angle DPB=120,
25) In the figure AB is the diameter of the circle such that Angle PAB= 40°.
26) In the figure O is the centre of the circle. Angle OAB and OCB are 20 and 55.
EXERCISE-B
1) In the given below,
2) In the following, figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose sides AB is the diameter of the circle, through A, B, C, D. If angle ADC =140.
3) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AB || CD and Angle B= 65.
4) The opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are in the ratio 4:5. Find the angles in degrees. 80, 100
5) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If angle BCD and ABD are 100 and 70, then
6) In the figure angle ADC=85
7) In the figure PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral.
8) In the figure angle DBC and BAC are 70, 40,
9) In the figure angle BDC and ACB are 35 and 40
10) In the given figure t∆ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB =AC and m(angle ABC)=50,
11) ABCD cyclic quadrilateral in which AD|| BC. If angle A= 70,
12) in the given figure below angle ABD=70, angle ADB=30,
13) In the given figure below, angle ACB= 35, angle BDC= 50,
14) in ∆ ABC , BE perpendicular to AC and CF perpendicular to AB which intercept each other at P. if angle A= 40°, find the angle BPC. 140
EXERCISE- C
1) Are the following statements true or false:
a) A quadrilateral whose opposite angles are 85° and 115° is cyclic.
b) A parallelogram whose 1 angle is 100° is cyclic .
c) A rectangle is a cyclic quadrilateral.
d) A square is a cyclic quadrilateral.
e) A rhombus is a cyclic quadrilateral.
f) O is the circumcenter of the ∆ ABC and OD perpendicular to BC. Is angle BOD= angle A.
g) AB is the diameter of a circle and AC and BD are its two parallel chords. Is AD= BC
2) O is the circumcircle of the ∆ ABC . Find the value angleOBC+ angle BAC.
3) who is the circums centre of the triangle ABC find the value of angle OBC A + angle BAC
4) Find the area of a right angled triangle if the radius of a circumcircle is 2 cm. 6
5) Find area right angled triangle if the radius of the circumcircle is 5cn and altitude drawn to the hypotenuse is 4cm. 20
6) ∆ ABC is right angled at B . On AC, a point D is taisecond so that AD = DC and AB = BD. Find angle CAB. 60
7) In the adjoining figure ;
8) In the joining figure angle AOC=110;
9) In the adjoining figure PQ= PR and angle PQR=70
10) In the adjoining figure;
EXERCISE-D
1) In the given figure angle DBC=70 and BAC= 40
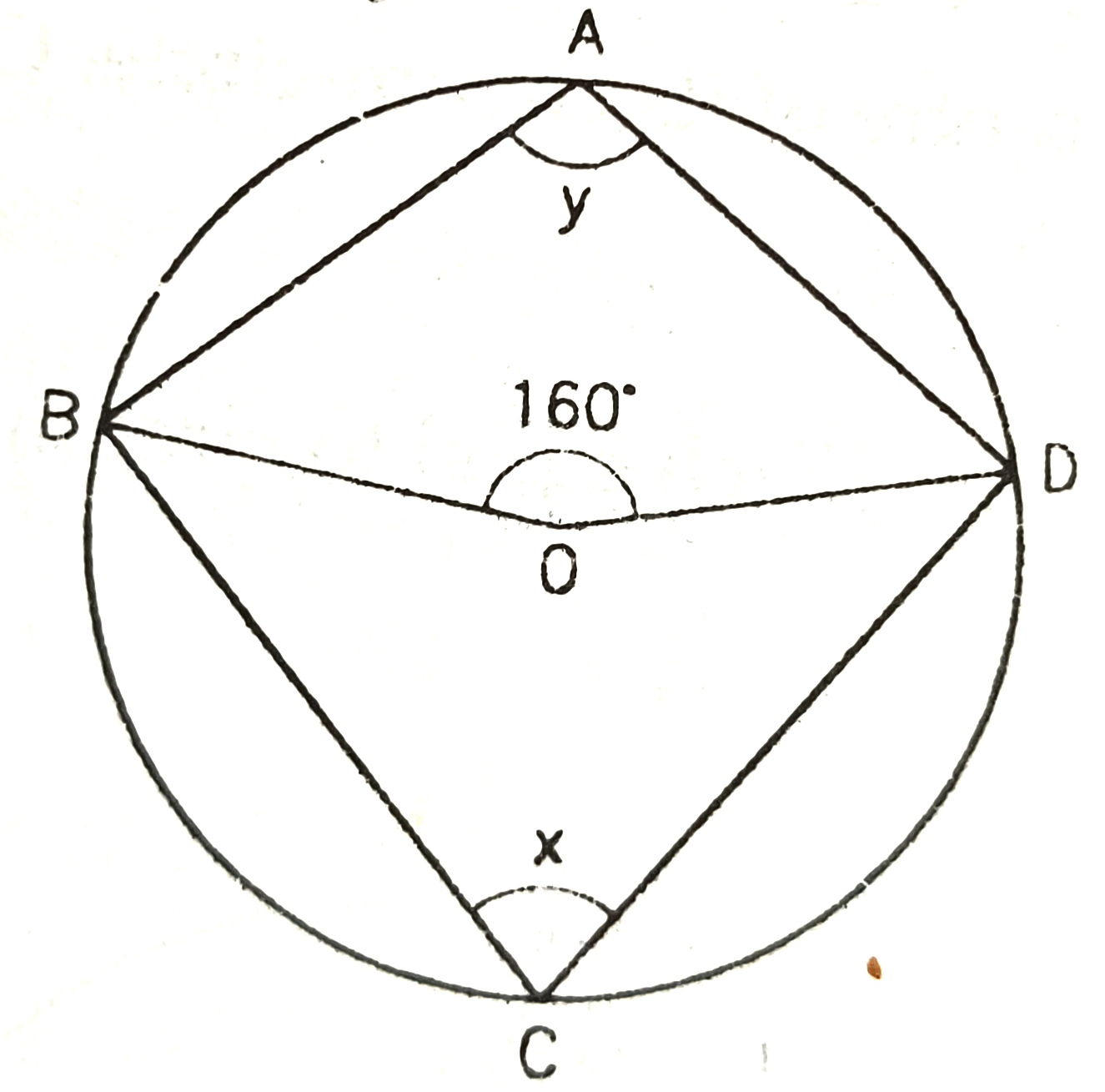
2) In the figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral; O is the centre of the circle. If angle BOD=160,
3) In the given figure ∆ ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB= AC and angle=50°.
4) In the figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose side AB is a diameter of the circle through A, B, C,D. If angle ADC=130,
5) In the figure C and D are points on the semi-circle described on BA as diameter. Given angles BAD, DBC are 70, 30.
6) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle. The angle subtended by the arc BCD at the centre is 140°. BC is produced to P.
7) In the figure BD = DC and angle DBC = 25.
8) In the given figure angle A=60 and angle ABC =80°,
9) In the figure ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle.
10) In the figure ∆ PQR is an isosceles triangle with the PQ= PR and angle PQR =35.
11) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle. if Angle BOD=160,
12) ABCD is a cycle quadrilateral. If angle BCD =100 and angle ABD=70.
13) In the given figure O is the centre of the circle.
14) In the figure AB and CD are diameters of a circle with centre O. If angle OBD=50
15) On a semi-circle with AB as diameter, a point C is taken, so that angle CAB=30. Find the the angles ACB and ABC . 90,600
16) In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD if AB|| CD and Angle B =70°, find the remaining angles. 70,110,110
17) In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, if angle A= 3 angle C. Find angle A. 135
18) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle and angle DAB=50.
19) In the figure angle BAC=60 and Angle BCA= 20
20) In the figure, if ABC is an equilateral triangle.
21) In the figure O is the centre of the circle. If angle CEA=30,
22) in the figure angle BAD =78 and angle DCF =x° and angle DEF=y°.
23) In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, if angle A - angle C=60°. Find the two smaller angles. 60
24) In the figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral.
25) if ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which
a) BC|| AD, angle ADC= 110 and BAC= 50°. Find angle DAC. 60
b) angle DBC=80° and angle BAC=40. Find angle BCD. 60
c) angle BCD= 100 and angel ABD=70. Find angle ADB. 30
26) ABCD is a cyclic trapezium with AD||BC. If angle B=70°, determine other three angles of the trapezium. 110,70, 110
MISCELLANEOUS
1) In the figure O is the centre of the circle.
2) In the figure O is the centre and angle=70.
3) ABCD cyclic quadrilateral EABF is a line such that angEAD=82°, ang FBC= 74, and angBDC=50°. find the obtuse angle between AC and BD. 108
4) Determine the angle a, b and c
105,13,62
5) O is the centre of the circle.
6) In figure, O is the centre of the circle and AP= BP.
7) In the figure, given AB= AC and angle ABC=68.
8) In figure O is the centre of the circle.
9) In the figure, given that PS= SR, ang RPS=54, and ang PRQ= 26,
10) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle.
11) In the figure, given AB|| DC.
12) In the figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. AE is drawn parallel to CB and DA is produced. If angle ADC =92, angle FAE= 20,
13) In the figure angle A =55° and angle C= 62° and the altitude BE produced meets the circle at D.
14) In the figure if y=x.
15) In the figure angle BCE=30.
16) In the figure I is the in-centre of ∆ ABC . AI when produced meets the circumcircle of triangle of ∆ABC in D. If angle BAC= 66 and angle ACB =80.
17) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle.
a) x b) y c) z d) none
17) In the figure AB=AD= DC=PB and angle DBC =20.
Find the angle ABD, APB. 20,20
18) in the figure O is the centre and AE the diameter of the semicircle ABCDE. If AB= BC and angle AEC=50°, then
19) In the figure, if y= 32 and z= 40,
20) In a triangle ABC, if angle A=60° and the bisectors of Angle B and angle C meets AC and AB at P and Q respectively and intersect each other at I, Find the value of BIC. 120
21) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If AC bisects both the angles A and C, then find the angle ABC. 90
22) In the figure, O is the centre of the circle and BC = OB.
a) y b) 2y c) 3y d) 4y e) none
23) In the figure, find angle BCD.
24) In the figure O is the centre of the circle arc ABC subtends an angle of 130° at centre O. AB is extended upto P.